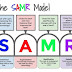
ICT Integration Model(TPACK Model ) 📓

🌸Concept of TPACK🌸
The TPACK framework, developed by Mishra and Koehler in 2006, stands for Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge. It emphasizes the integration of three key types of knowledge essential for effective teaching with technology:
Technological Knowledge (TK): This refers to an understanding of how to use technology effectively. It includes knowledge of different digital tools, software applications, hardware, and their functions. TK is about knowing how to operate and troubleshoot technology.
Pedagogical Knowledge (PK): This is knowledge about teaching strategies, methods, and approaches. It includes an understanding of instructional practices, classroom management techniques, assessment methods, and how students learn best. PK focuses on the art and science of teaching.
Content Knowledge (CK): This pertains to subject matter expertise. It involves a deep understanding of the concepts, principles, and theories within a particular discipline or content area. CK encompasses knowledge of curriculum standards, subject-specific terminology, and the relationships between different concepts.
The TPACK framework suggests that effective teaching with technology occurs at the intersection of these three knowledge domains:
Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (TPK): This refers to the knowledge of how to use technology to facilitate effective teaching and learning experiences. It involves understanding how specific technological tools and resources can be integrated into pedagogical practices to support learning goals.
Technological Content Knowledge (TCK): This involves understanding how technology can be used to represent and convey subject matter content in ways that enhance student understanding and engagement. It includes knowing how to select and use appropriate digital resources, simulations, multimedia, and other technology-based content to teach specific concepts effectively.
Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK): This is the understanding of how to teach particular subject matter content in ways that are meaningful and effective for students. It involves knowing how to adapt instructional strategies, activities, and materials to address the diverse needs, interests, and learning styles of students within a specific content area.
Reflection
We learned about the TPACK model where I learned that it is a frame that emphasizes the importance of integrating all three types of knowledge technological, pedagogical, and content too develop effective teaching practices that leverage the affordances of technology to enhance student learning outcomes. It encourages educators to consider how technology can be used strategically to support and enhance their teaching methods and the delivery of content in ways that promote deeper understanding, critical thinking, and engagement among students.
Integrating TPACK into primary education means:
1. Providing teachers with training in technology, pedagogy, and subject matter.
2. Ensuring tech use aligns with curriculum goals.
3. Teaching teachers to select age-appropriate tech tools.
4. Promoting engaging pedagogical strategies with tech.
5. Using tech to personalize learning and assess progress.
6. Educating on digital citizenship and safety.
7. Facilitating collaboration and communication through technology.
💛Lesson Plan 💜
Lesson Teacher name : Sangay Choden
Subject: Mathematics
Topic: Division as equal grouping
Class: 4 Time: 50 mins
👉Teaching Learning activities:
👉 ICT model : TPACK MODEL
👉 Previous Knowledge:
• Students already have the prior knowledge of basic multiplication and division concepts,
including the meanings of "equal sharing" and "repeated addition".
👉 Lesson Objective:
By the end of the lesson, the student will be able to :
a) apply the concept of division as equal grouping correctly after doing the group works;
b) work on solving division problems by watching the video on grouping the counters equally
after teacher's instruction;
c) exhibit a positive attitude towards division as a useful mathematical tool effectively after solving
some division problems.
👉 Engage (5 minutes):
• To begin the lesson, I will ask if the students have ever shared things in their life by dividing it
equally among themselves.
• Then, I will introduce the concept of division as equal grouping through a simple video
Video link: https://www.google.com/search?q=simple+video+on+division+for+class+1&sca_esv=3f9120de01b80e72&rlz=1C1FKPE_en-GBB
T1099BT1099&biw=1366&bih=641&tbm=vid&sxsrf=ACQVn0--NyGVOEl73qfnd8XjDVn9q7dPhw%3A1713964878521&ei=TgcpZve6
H9r04-EPya2LyAg&ved=0ahUKEwj3mffd-NqFAxVa-jgGHcnWAokQ4dUDCA0&uact=5&oq=simple+video+on+division+for+c
lass+1&gs_lp=Eg1nd3Mtd2l6LXZpZGVvIiRzaW1wbGUgdmlkZW8gb24gZGl2aXNpb24gZm9yIGNsYXNzIDEyBRAhGKABMgUQIRigATIFEC
EYoAEyBRAhGKABMgUQIRigATIFECEYnwUyBRAhGJ8FSPkbUNsCWJMZcAB4AJABAZgBsQagAYQmqgELMi0yLjIuNC4yLjG4AQPIAQD4A
QGYAgqgApUjwgIGEAAYFhgewgILEAAYgAQYhgMYigXCAgcQRigARgKmAMAiAYBkgcLMi0yLjIuNC4xLjGgB69W&sclient=gws-wiz-video#
• I will also show them a video on how top divide counters e.g. in equal group.
Video link: https://www.google.com/search?q=video+on+division+of+counters+equal+group&rlz=1C1FKPE_en-GBBT1099BT1099&oq
=video+on+division+of+counters+equal+group&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOdIBCTE5MDQyajBqN6gCCLACAQ&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8#
👉Explore (10 minutes):
Activity 1:
After watching the video, I will let the students explore the provided counters and ask them to group
the provided 10 counters equally into different groups.
• For this I will ask students to count the number of counters in each group and to check if they
have made equal groups.
• * If some students find it difficult or didn't get the instruction clearly, I will provide support and
repeat the instructions again.
• After that I will let some students share their answers.
👉 Explain (10 minutes):
• I will present the ppt
Link: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1SXiG1evAqbwBCbWU-
iEY2Qm65m3lOyRA/edit?usp=drive_link&ouid=106087743574103077226&rtpof=true&sd=true
• I will show an example of division on the board and explain the different parts of a division
problem (dividend, divisor and quotient) in division as equal grouping.
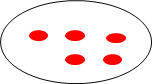
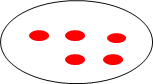
Where,
• 10(Dividend)- Total number
• 2(Divisor)- Number of equal groups. Eg) 10 ÷ 2 = 5
* 5(quotient)-size of the groups.
👉 Elaborate (12 minutes):
Activity 2 :
👉 Follow- up activity (6 minutes) :
• Students will have to write the answers on the worksheet.
• Here, I will circulate around the room to monitor and to ensure that all
the students are participating and are using counters to solve the problem.
• If some students find difficulty, I will ask the group who got the correct
answer to help the other slow learners
👉 Evaluate (7 minutes):
• To assess the students' understanding, I will let them share and explain their
answers in the classroom.
• To wrap up the lesson, I will ask the students to share one thing they learned
about division as equal grouping and let them state one importance of equal grouping.
• I will assign them Homework (Individual work) that is to solve the questions in
practicing and applying on page no. 118.
👉👉👉Here's how the lesson plan integrates the TPACK framework:
👉Technology:
Incorporating technology into this lesson could involve using PPT and video clips like
those used in the above. To reinforce the concept of division as an equal grouping
In addition, it visually illustrates the concept, making it more accessible and engaging for
students.
👉Pedagogical Strategy:
The pedagogical strategy in this lesson is the problem-solving method where the students
focus on hands-on, experiential learning through the use of manipulatives (counters), visual
aids (chart paper, ppt, and video clips ), and group work. Furthermore, the online quizzes and
the use of worksheets and class discussions encourage active participation and reflection,
reinforcing learning outcomes.
👉Content Knowledge:
The lesson content is centered around the fundamental concepts of division, including dividend,
divisor, and quotient, as well as the application of division as an equal grouping. By building on students' prior knowledge of sharing concepts, the lesson scaffolds learning to help students grasp
the new concept effectively. Clear explanations, guided practice, and opportunities for application ensure that students develop a solid understanding of division as equal grouping by the end of the lesson.
Overall, by integrating technology to enhance learning experiences, employing effective
pedagogical strategies, and building on solid content knowledge, this lesson plan optimizes the
TPACK framework to facilitate meaningful learning outcomes for students😊😊😊.
►►THANK YOU ◄◄
.jpg)